What Does Collate Mean in Printing?
You’re printing a 10-page report. You need five copies. You see a box labeled “collate.” Should you check it? This small choice saves you 15-30 minutes of manual sorting. Office workers waste 2-3 hours monthly organizing uncollated documents. A survey of 500 businesses found that 73% prefer collated printing for multi-page documents. The feature cuts document preparation time by 80%.
What Does Collate Mean in Printing
Collating organizes your printed pages in order. Your printer arranges each complete set before printing the next. Here’s a real example. You print three copies of a 5-page document. With collating ON, you get:
- Copy 1: pages 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Copy 2: pages 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Copy 3: pages 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Without collating, you receive:
- All page 1s together
- All page 2s together
- All page 3s together
- All page 4s together
- All page 5s together
You must manually sort the pages yourself.

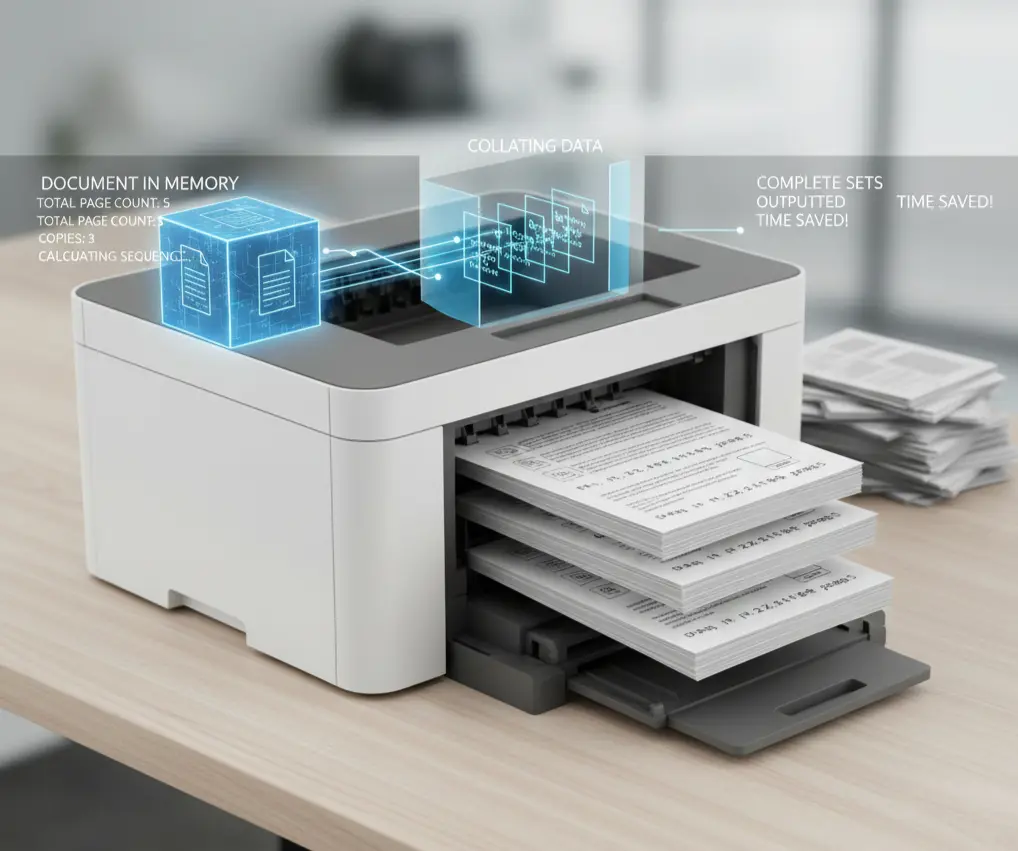
How Collating Actually Works
Your printer stores the document in memory. It reads the total page count. It calculates the printing sequence. Then it outputs complete sets. Modern printers handle this automatically. Older models might struggle with large jobs. Memory capacity matters here. The process takes slightly longer. Your printer organizes data differently. The trade-off saves your time later.

When to Use Collated Printing
Collating shines in specific situations.
Meeting Materials Print 20 copies of your presentation. Each attendee gets a ready-to-use packet. No sorting required.
Classroom Handouts: Teachers print worksheets for 30 students. Every student receives complete materials immediately.
Business Proposals: Send proposals to multiple clients. Each document is perfectly organized by the printer.
Training Manuals HR departments distribute employee handbooks. Collating creates ready-to-distribute copies.
Event Programs Conference organizers print schedules and materials. Attendees receive organized packets.
When to Skip Collating
Some situations work better without collating. You’re printing single-page flyers. You need 500 copies of one form. You plan to add dividers manually. You’re printing different quantities of each page. Uncollated printing runs faster in these cases.
How to Turn On Collate
Windows Users
Open your document. Press Ctrl + P. Click “Printer Properties.” Find the “Finishing” tab. Check “Collate.” Enter copy number. Click Print.
Mac Users
Open your document. Press Command + P. Click “Show Details.” Find “Copies & Pages.” Check “Collated.” Enter copies needed. Click Print.
Microsoft Word
The print dialog shows collate options directly. No deep settings needed.
PDF Readers
Adobe and other PDF apps include collate in basic print settings. Most modern software makes this easy.
Collated vs Uncollated: Quick Comparison
Collated Printing Benefits
- Documents ready immediately.
- Zero manual sorting.
- No missing pages.
- Saves significant time.
- Perfect for distribution.
Printing Drawbacks
- Slightly slower printing.
- Requires printer memory.
- Not ideal for single pages.
Uncollated Printing Benefits
- Faster print speed.
- Uses less memory.
- Good for forms.
- Better for selective printing.
Uncollated Printing Drawbacks
- Manual sorting needed.
- Time-consuming assembly.
- Risk of page mix-ups.
- Not distribution-ready.
Common Collating Problems and Fixes
Pages Print in Wrong Order
Your printer lacks sufficient memory. Try these solutions:
- Reduce copies per job.
- Lower print quality.
- Print in smaller batches.
- Close other programs.
- Restart the printer.
Collate Option Unavailable
Your printer doesn’t support this feature. Basic models often lack collating. You have two choices:
- Sort pages manually.
- Upgrade your printer.
Slow Printing Speed
Collating requires more processing. This is normal behavior. Speed it up by:
- Using draft mode.
- Reducing image quality.
- Printing fewer copies at once.
- Upgrading printer firmware.
Copies Come Out Blank
Check your ink levels. Verify paper is loaded correctly. Ensure proper driver installation. Run printer diagnostics.
Tips for Better Collated Printing
Check Preview First. Always verify settings before printing. The preview shows the exact output order.
Load Enough Paper. Calculate the total sheets needed. A 10-page document with 5 copies needs 50 sheets.
Use Quality Settings Wisely. Draft mode speeds up internal documents. Normal mode works for client materials.
Save Your Preferences. Create printing presets. Include collate in your default settings.
Test Small Batches Print 2-3 copies first. Verify correct collation. Then print the full quantity.
Monitor Memory Usage: Large color documents need more memory. Simplify graphics if issues occur.
Keep Drivers Updated. Manufacturers fix collating bugs in updates. Check quarterly for new versions.

Understanding Printer Memory
Memory determines collating capability.
Small jobs need minimal memory. Large jobs require substantial capacity. Color pages use more memory than black and white. High-resolution images demand extra space. Entry-level printers: 128MB-256MB. Mid-range printers: 512MB-1GB. Professional printers: 2GB or more. More memory means better collating performance.
Professional vs Home Printing
Home printers handle basic collating. They manage standard documents well. Limitations appear with large jobs. Professional printers excel at collating. They process hundreds of pages. They maintain speed and accuracy. And rarely encounter memory issues. Copy centers use industrial collating equipment. These machines finish and bind simultaneously.
Mobile Printing and Collating
Mobile devices support collating, too. iPhone and Android printing apps include this option. Cloud printing services maintain collate settings. Wireless printers accept collated mobile jobs. The process mirrors desktop printing. Settings appear in print dialogs. Enable collation before sending.
Conclusion
Collating organizes printed documents into complete, sequential sets. This feature saves time and eliminates manual sorting. Enable it when printing multiple copies of multi-page documents. Your printer handles the organization automatically. The result is distribution-ready materials requiring zero assembly. Understanding this simple function transforms your printing efficiency and workflow.